Windows are a big part of any home. They let in light and fresh air and provide a clear view outside. But many people don’t know the names of all the parts that make up a window.
One important part is the window sash. It plays a key role in how a window works and how easy it is to use.
Understanding what is a window sash becomes essential when you’re considering window repairs, replacements, or upgrades to your home.
In this blog, we’ll see the window sash in detail, breaking down its components, types, and functionality to give you a complete understanding of this vital window element.
What is a Window Sash?
A window sash is the frame that holds the glass panes in a window. It can be fixed or movable, depending on the window style.
In traditional double-hung windows, for example, the upper and lower sashes slide vertically to allow airflow.
In casement windows, the sash is hinged and swings outward. The sash plays a major role in a window’s structure, insulation, and overall performance.
It keeps the glass secure, helps seal out drafts, and contributes to the window’s appearance.
Sashes are typically made from materials like wood, vinyl, aluminum, or fiberglass, each offering different benefits for durability, maintenance, and energy efficiency.
Breaking Down the Components of a Sash Window
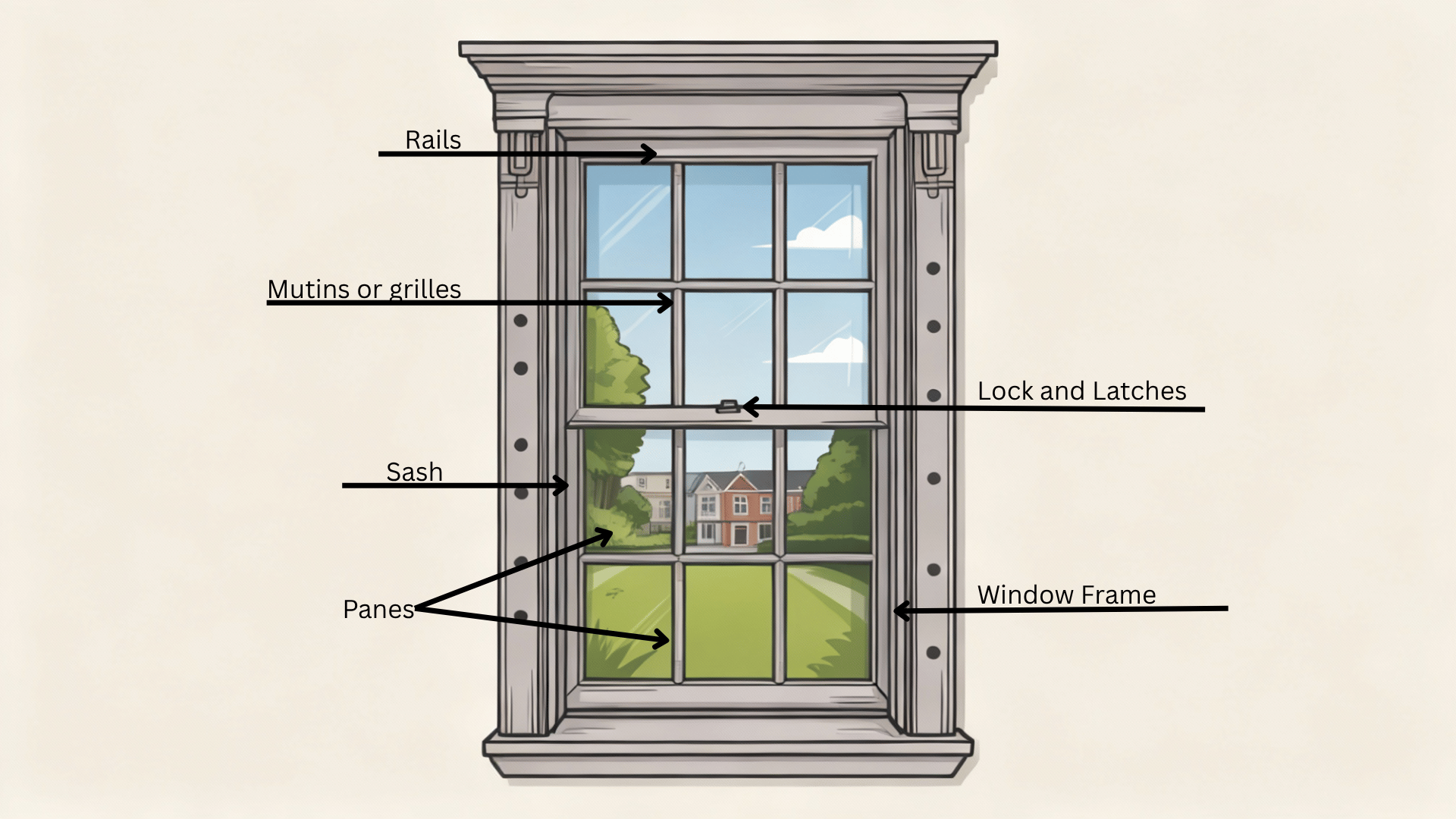
Every sash window includes specific elements that contribute to its strength, operation, and energy efficiency. Here’s a simple breakdown.
- Sash: The movable or fixed framed section holding the glass panes, providing structure, operation, and insulation within the window. wooden frames
- Window Frame: The outer structure surrounding the sash, supporting the window, securing it to the wall, and ensuring stability and proper alignment.
- Stiles: Vertical components on each side of the sash, providing strength, guiding movement, and helping maintain the sash’s overall shape.
- Rails: Horizontal top and bottom parts of the sash that support the glass, connect stiles, and allow smooth sash movement.
- Muntins/Grilles: Thin bars dividing glass panes visually or structurally, creating traditional patterns and enhancing the decorative style of the window.
- Balances / Cords / Weights: Mechanisms that assist sash movement, counterbalancing weight for smooth operation in traditional or modern window designs.
- Weatherstripping: Sealing material around the sash edges, reducing drafts, improving insulation, and enhancing overall window energy efficiency.
- Locks and Latches: Hardware securing the sash closed, improving safety, tightening seals, and helping maintain proper window alignment.
Types of Window Sashes
From classic double-hung designs to modern sliding styles, window sashes vary widely in how they open and operate.
1. Single-Hung Sash
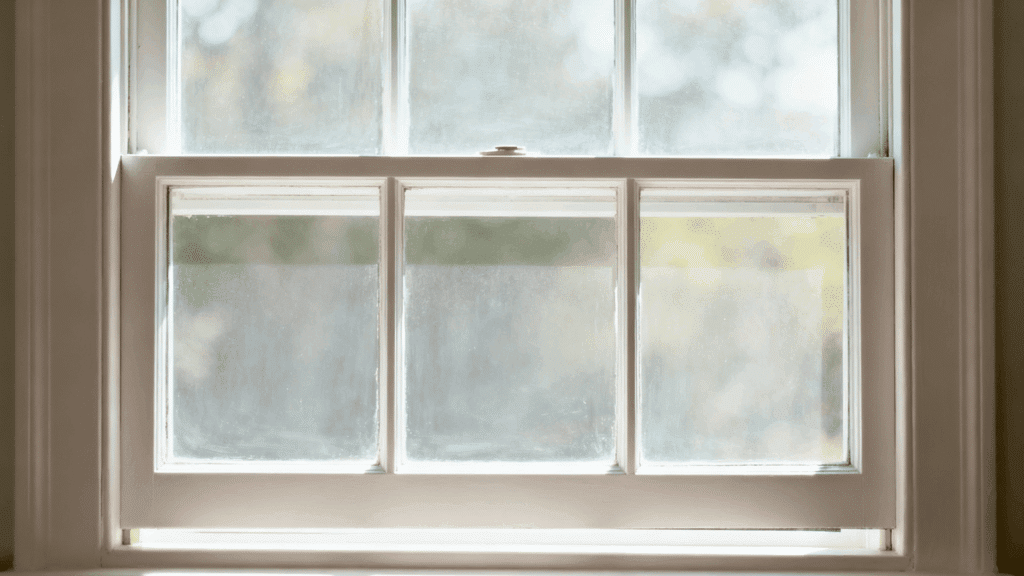

Single-hung windows feature two sashes stacked vertically, but only the bottom sash is operable and can move up and down.
The top sash remains fixed. This design is one of the most economical window options and requires minimal maintenance.
Single-hung sashes are popular in traditional and budget-conscious homes, offering adequate ventilation while maintaining a classic appearance that complements various styles.
2. Double-Hung Sash
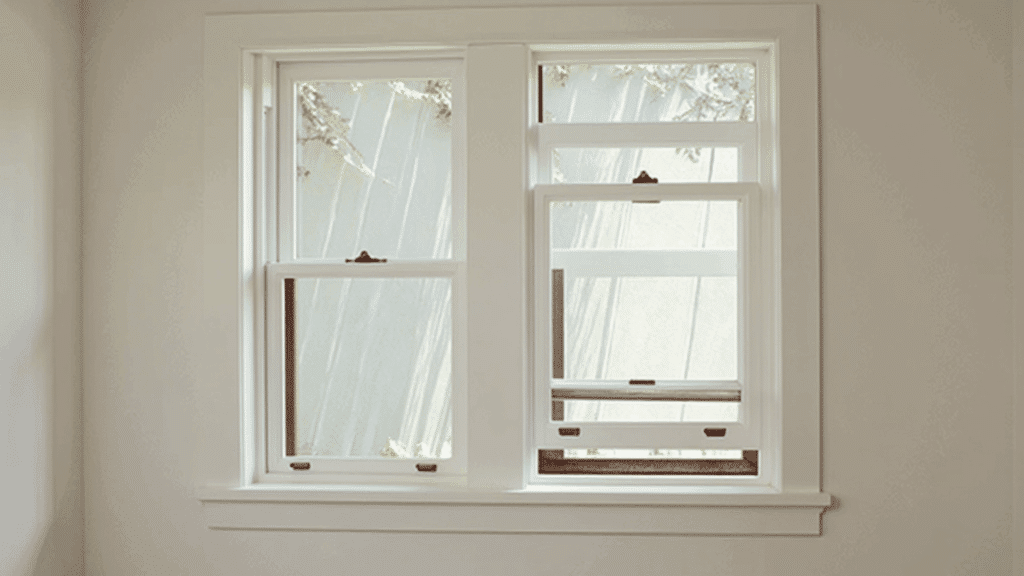

Double-hung windows contain two movable sashes that both slide vertically, allowing you to open either the top or bottom sash independently.
This versatility provides superior ventilation control and makes cleaning easier, as many models feature tilt-in sashes for exterior cleaning from inside.
Double-hung sashes are extremely popular in residential construction due to their flexibility, ease of use, and ability to direct airflow effectively throughout your living spaces.
3. Casement Sash
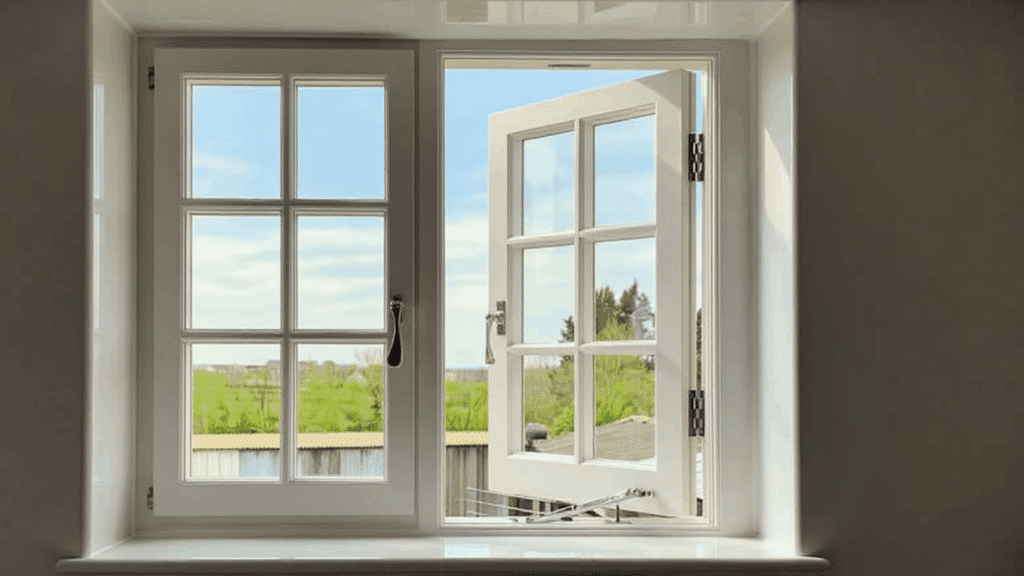

Casement sashes are hinged on one side and swing outward like a door, operated by a crank or a push bar.
They open completely to provide maximum ventilation and unobstructed views. Casement windows create an excellent seal when closed, making them highly energy-efficient.
Their design catches breezes and directs airflow into your home, making them ideal for areas where you want to maximize cross-ventilation and natural cooling.
4. Sliding Sash
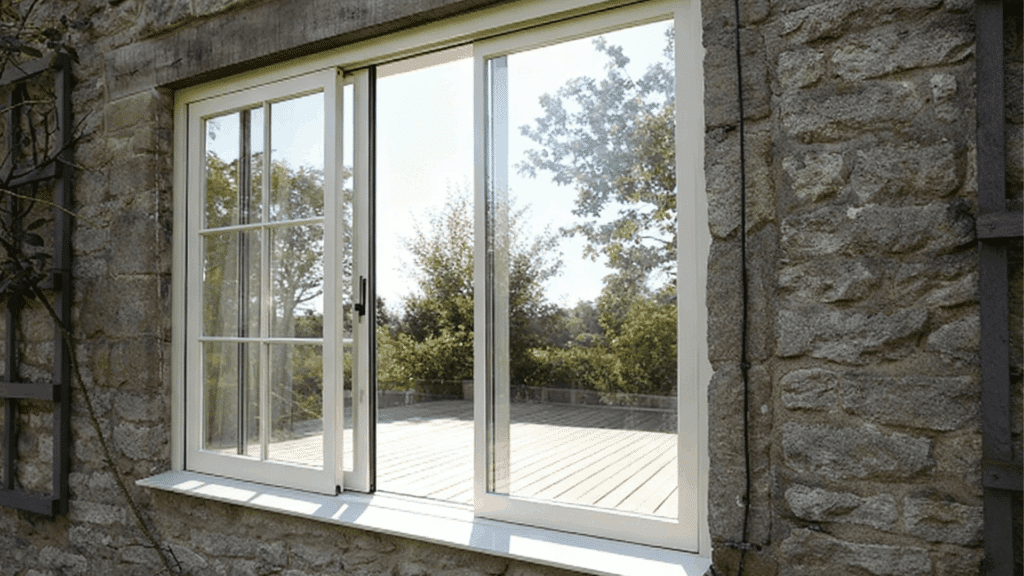

Sliding sashes move horizontally along tracks, with one or both panels able to glide left or right. These windows are perfect for spaces with limited clearance.
Sliding sashes offer easy operation, contemporary aesthetics, and wide viewing areas.
They’re commonly used in modern homes and are particularly popular for accessing decks, balconies, or garden areas where space efficiency matters.
5. Awning Sash
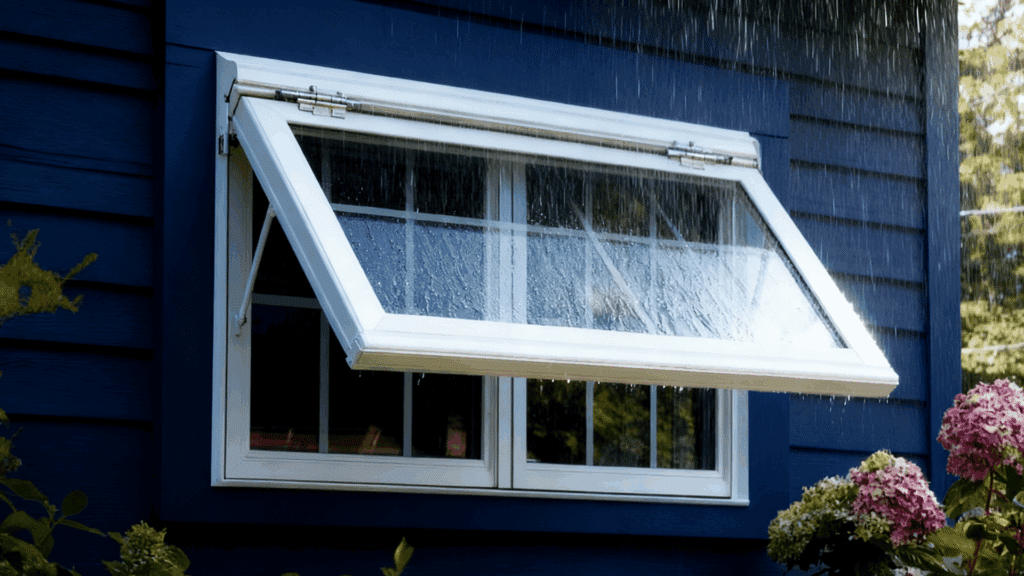

Awning sashes are hinged at the top and open outward from the bottom, creating a protective awning effect. This design allows you to keep windows open even during light rain.
Awning windows provide excellent ventilation while maintaining privacy, making them ideal for bathrooms or basements.
They’re often installed higher on walls or combined with larger fixed windows for added functionality.
6. Hopper Sash
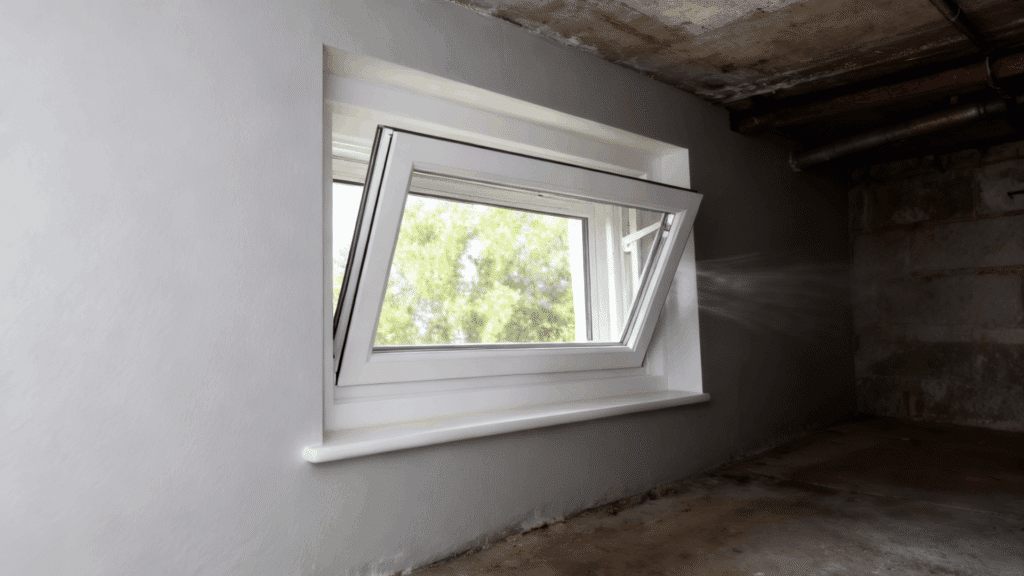

Hopper sashes are hinged at the bottom and tilt inward from the top, essentially functioning as an inverted awning window.
These windows are typically installed in basements, bathrooms, or small utility spaces where limited wall area exists. Hopper sashes are easy to operate and clean since they open inward.
Their design provides good ventilation while maximizing security. They’re particularly useful in below-grade applications where exterior access is restricted.
Maintenance Tips for Longer-Lasting Sashes
With a few easy maintenance steps, you can protect your window sashes and keep them looking and performing their best.
- Inspect regularly for cracks, rot, or warping: Catching early damage prevents costly repairs later.
- Clean tracks and moving parts: Dirt buildup makes sashes harder to open and can wear out hardware.
- Repaint or reseal wooden sashes: A fresh coat protects against moisture, rot, and sun damage.
- Lubricate hinges, locks, and sliders: Smooth operation reduces strain on the sash and frame.
- Check and replace worn weatherstripping: This keeps drafts out and maintains energy efficiency.
- Wipe down glass and sash surfaces: Prevents grime buildup and helps you spot issues early.
Conclusion
Understanding what is a window sash helps you to make better decisions about window maintenance, repairs, and replacements throughout your homeownership journey.
Take a quick look at your windows. If a sash is loose, damaged, or hard to move, it may be time to fix or replace it.
Catching small issues early can save money and trouble later
Now that you’re equipped with this knowledge, take a moment to inspect your window sashes for any signs of wear or damage. Your home’s comfort and energy bills will thank you!

