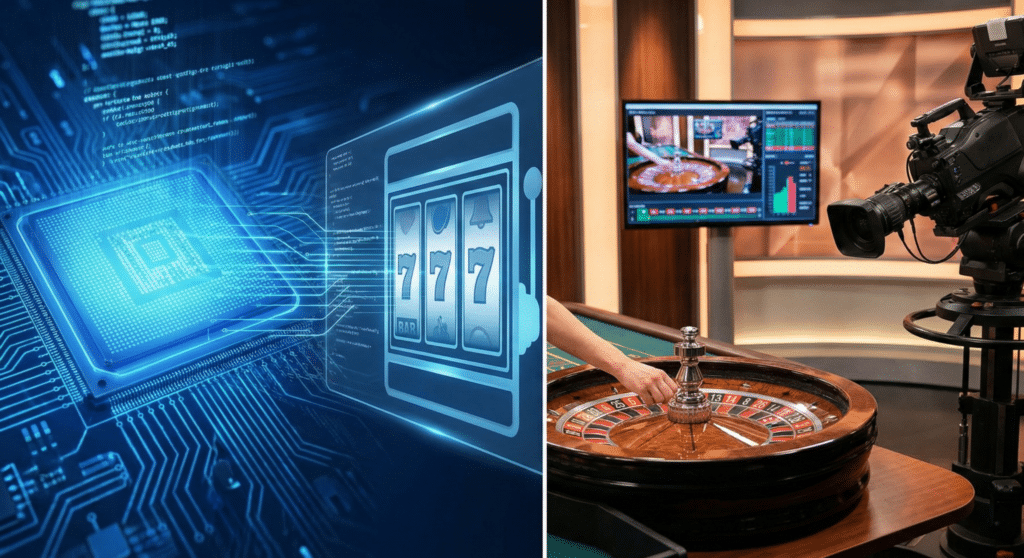
The Technological Transformation of Digital Gaming
The digital gaming landscape has undergone significant transformations since its inception. Initially, the translation of traditional table games and slots into an online format relied entirely on software mimicking physical probabilities. Today, however, a substantial portion of the sector has moved toward hybrid models that blend digital interfaces with real-world video streaming.
Understanding the distinction between these two primary formats—standard digital games governed by algorithms and live dealer experiences—requires looking beneath the surface at the technologies that power them. While the end result for the user may appear similar on screen, the mechanisms determining outcomes and the overall pacing differ fundamentally.
The Foundation of Standard Digital Play: Random Number Generators (RNGs)
For decades, the backbone of online gaming has been the Random Number Generator (RNG). Whether it is a digital slot machine, a virtual blackjack table, or a roulette wheel simulation, an RNG is the microprocessor engine that determines the outcome of every single event.
An RNG is a piece of software designed to generate a sequence of numbers or symbols that lack any discernible pattern. Crucially, these outcomes must be statistically independent; the result of a previous spin or hand has absolutely no bearing on the next one.
The Role of RTP in Algorithmic Environments
In these purely digital formats, the game’s design is mathematically rigid. The concept of Return to Player (RTP) is hardcoded into the software. RTP is a theoretical percentage that indicates how much of the wagered money a game is programmed to pay back to players over an extended period of time.
For example, a digital slot with a 96% RTP is designed, over millions of spins, to return $96 for every $100 wagered. It is vital to understand that this is a long-term statistical average, not a guarantee for a single session. In the short term, volatility determines the variance of outcomes, leading to swings in both directions. In RNG games, these parameters are fixed by the software developers and audited by third-party testing labs to ensure the algorithm functions within its stated parameters.
The Live Bridge: Merging Physical Actions with Digital Interfaces
The emergence of “Live Dealer” or “Live Casino” formats represented a pivot away from pure reliance on RNGs for determining results in table games. This format attempts to replicate the environment of a physical gaming floor by streaming human dealers operating real equipment in real-time.
This setup requires vastly more complex infrastructure than standard software-based games. It involves custom-built studios, high-definition multi-camera setups, and specialized lighting. However, the most critical technological component in this ecosystem is the bridge that translates physical reality into digital data.
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) Technology
The core technology that makes live streaming interactive is Optical Character Recognition (OCR). As a human dealer shuffles cards or spins a roulette wheel, every action is captured by cameras. OCR technology instantly scans the physical cards as they are dealt or identifies the pocket where the roulette ball lands.
This visual information is immediately converted into digital data. This data is what allows the user interface on the player’s screen to update instantly, showing the card values or winning numbers. If a player is holding a winning hand based on the physical cards on the table, the software recognizes it via the OCR feed and processes the result automatically.
In this environment, the “RNG” is replaced by physics. The shuffle of a deck or the deceleration of a ball dictates the outcome, reintroducing physical variables that are absent in purely algorithmic games.
Comparing the User Experience Across Formats
The technological underpinnings of RNG versus Live formats lead to distinct differences in how the games are experienced by the end user. These differences often dictate which format a player prefers depending on their desired level of engagement and pacing.
Pacing and Speed
Algorithmic RNG games are inherently faster. Because there are no physical actions to perform—no waiting for other players to act, no manual shuffling, and no physical dealing time—a hand of digital blackjack or a slot spin can be completed in seconds. The player has complete control over the tempo of the session.
Conversely, live dealer games are bound by physical limitations. The pace is dictated by the dealer and the collective actions of other participants at the virtual table. This results in a slower, more deliberate rhythm that mirrors a brick-and-mortar environment.
The Element of Trust and Interaction
One of the primary drivers for the adoption of live streaming was a segment of users who remained skeptical of purely software-based outcomes, despite third-party auditing. Seeing physical cards being dealt provides a layer of visual transparency that an algorithmic result cannot offer.
Furthermore, the live format introduces a social dimension. Users can interact with the dealer and sometimes other players via chat functions. This transforms a solitary activity into a somewhat communal one. Because the quality of streaming, the professionalism of dealers, and the specific table limits can vary significantly between different software providers, specialized platforms like LiveCasinoComparer com exist to aggregate this data for users researching specific game variations.
Bandwidth and Technical Requirements
A final consideration is the technical demand placed on the user’s hardware. Standard RNG games are generally lightweight, requiring minimal data transfer once the game assets are loaded. They function well even on slower connections.
Live streaming formats, by contrast, are data-intensive. They require a stable, high-speed internet connection to maintain a clear video feed and ensure that bets are registered instantly without latency issues, which can disrupt real-time gameplay.
Conclusion
The coexistence of RNG-based games and live dealer streams provides a spectrum of options within the digital gaming space. The former offers speed, immediate access, and mathematically defined parameters, while the latter utilizes complex broadcast technology to offer transparency, a slower pace, and a human element. Both rely on sophisticated, albeit very different, technologies to ensure fair and functional gameplay in a remote setting.