In this guide, we will walk you through the steps to troubleshoot your vehicle’s flashing parking brake light.
As someone who has experienced this issue firsthand and helped countless others resolve it, we know how frustrating and worrisome it can be.
By following the simple, step-by-step instructions in this article, you can identify the cause of your flashing parking brake light and fix it quickly, saving you time and money.
Let’s get started!
Common Causes of a Persistent Parking Brake Light
| Cause | Description | Common Signs |
|---|---|---|
| Faulty Parking Brake Switch | A switch that incorrectly signals that the parking brake is engaged even when it’s not. | The parking brake light stays on after disengagement. |
| Low Brake Fluid Level | Insufficient brake fluid in the system, affecting hydraulic pressure. | The brake light is on; it is possible that brake performance drops. |
| Bad Brake Fluid Level Sensor | The sensor fails to report brake fluid levels, causing false alerts accurately. | Inconsistent brake light activity. |
| Stuck or Frozen Cables | Cables that activate the parking brake might be stuck or frozen, preventing full disengagement. | The parking brake feels stuck; the light remains on. |
| Faulty Wiring or Electrical Issues | Poor electrical connections or damaged wires lead to false signals or failures in the system. | Flickering brake light; random light activation. |
| ABS Malfunctions | Issues within the Anti-Lock Braking System that indirectly trigger the parking brake light. | ABS light may also be illuminated. |
Step-by-Step Guide to Troubleshooting Your Parking Brake Light

1. Preliminary Checks
Before diving into more complex troubleshooting, start with these basic checks:
- Check Parking Brake Engagement: Make sure the parking brake is fully disengaged. This may seem obvious, but a common oversight can cause the light to remain on.
- Brake Fluid Level: Check the brake fluid reservoir and verify that the fluid is at the proper level. Low brake fluid can trigger the brake light, so top it off if necessary.
- Visual Inspection of the Brake System: Perform a visual inspection of the brake pads, cables, and connections. Look for signs of wear, damage, or anything affecting the brake system’s functionality.
2. Inspecting Mechanical Components
If the preliminary checks don’t resolve the issue, move on to inspecting the mechanical components of the parking brake system:
- Brake Handle and Cables: Check if the brake handle is fully lowered when disengaged. Inspect the cables for any signs of damage, rust, or sticking that could prevent proper operation.
- Parking Brake Mechanism: Ensure the brake mechanism releases completely when the handle is lowered. Check for misalignment or malfunctioning components that could keep the system engaged.
3. Electrical System Checks
Electrical issues can often cause the parking brake light to malfunction. Here’s how to check these components:
- Test the Parking Brake Switch: Using a multimeter, test the brake switch for continuity. If the switch fails to show proper readings, it may need to be replaced.
- Inspect Wiring and Connections: Examine the wiring harness and connections to the parking brake system. Look for frayed wires, loose connectors, or signs of corrosion that could cause false signals to be sent to the dashboard light.
4. Advanced Diagnostics
If the above steps don’t identify the problem, you may need to perform more advanced diagnostic tests:
- ABS System Check: Issues with the Anti-Lock Braking System (ABS) can sometimes affect the parking brake light. Use a diagnostic scan tool to read any ABS fault codes related to the problem.
- Sensor Testing: Use the appropriate diagnostic tools to test the functionality of the brake fluid level sensor and other related sensors. Faulty sensors can send incorrect signals, causing the parking brake light to stay on.
DIY Fixes for Parking Brake Light
Before seeking professional help for a persistent parking brake light, there are several DIY fixes you can attempt.
These initial steps often resolve common issues, saving you time and money. Let’s explore these fixes in detail.
1. Ensuring the Parking Brake is Fully Disengaged
Start by visually confirming that the parking brake lever or pedal is fully disengaged. Look for any unusual positioning or misalignment that might suggest an issue.
Physically check the lever or pedal for resistance or an unusual feel when disengaging the parking brake. If you notice stiffness or difficulty moving the lever or pedal, it may indicate a problem with the mechanism.
2. Checking and Refilling Brake Fluid
The brake fluid reservoir is typically located near the engine. The exact location is in your vehicle’s owner’s manual.
Once you’ve located the reservoir, check the fluid level against the max and min markers on the side of the container.
If the fluid is below the minimum marker, it must be refilled.
Consult your owner’s manual for the recommended type of brake fluid for your vehicle.
Carefully add the brake fluid to the reservoir until it reaches the appropriate level between the minimum and maximum markers, being careful not to overfill the reservoir.
3. Inspecting the Parking Brake Switch and Sensors
Locate the parking brake switch and any associated sensors. Your vehicle’s manual should provide information on their exact location.
Examine the switch and sensors for any visible damage, wear, or corrosion that might affect their function. If you notice any issues, these components may need to be replaced.
Use a multimeter to test the parking brake switch for proper operation and continuity. Set the multimeter to the continuity setting and place the probes on the switch’s terminals.
The multimeter should indicate continuity when the switch is engaged and no continuity when disengaged.
If the readings are inconsistent, the switch may be faulty.
Resetting Your Parking Brake Light
1. Manual Reset
The manual reset procedure may vary depending on your vehicle, but it generally involves the following steps:
- Turn the ignition on and off a few times.
- Engage and disengage the parking brake several times (consult your manual for the exact number).
- Drive the vehicle a short distance to see if the light turns off.
Refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual for specific reset procedures unique to your make and model. Some vehicles may have slightly different steps or additional requirements.
2. Electronic Systems
Some vehicles have electronic parking brake systems that automate certain functions, including the parking brake light reset. These systems may require different reset procedures.
- Reset via Vehicle Interface: Navigate through the dashboard or central console screen menus to find the parking brake light reset option. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the reset process.
- Using Diagnostic Tools: Connect the diagnostic tool to your vehicle’s OBD-II port (usually located under the dashboard) and follow the device’s instructions to reset the parking brake light.
Is It Safe to Drive When the Brake Warning Light Comes On?

Driving with the brake warning light can be dangerous and is not recommended.
Here’s what you need to know about the safety risks and what actions to take if the light comes on while driving.
1. Immediate Safety Risk
When the brake warning light illuminates, it indicates a potential issue with your vehicle’s braking system.
Depending on the severity of the problem, your braking capability may be impaired, increasing the risk of accidents.
Reduced braking power can lead to longer stopping distances and difficulty controlling the vehicle, especially in emergencies.
2. Assess the Severity
Not all brake warning lights indicate the same level of urgency.
For example, a parking brake light that stays on may suggest a less immediate danger than a warning light, indicating a complete failure of the brake system.
However, it’s essential to err on the side of caution and address any brake-related warning lights promptly.
3. Recommended Actions
If the brake warning light comes on while you’re driving, follow these steps to ensure your safety and the safety of others on the road:
- Safely pull over to the side of the road as soon as possible.
- Turn on your hazard lights to alert other drivers.
- Check your vehicle’s brake system for visible issues like leaking fluid or damaged components.
- If you cannot identify or resolve the problem, do not attempt to drive the vehicle further.
- Call for roadside assistance or have your vehicle towed to a mechanic for a thorough inspection and necessary repairs.
When to Seek Professional Help

Scenarios where professional diagnostics and repair are recommended:
- Persistent warning lights: If you’ve gone through the troubleshooting steps and the parking brake light remains on, it’s time to seek professional help. A qualified mechanic can use specialized diagnostic tools to pinpoint the exact cause of the issue and recommend the appropriate repairs.
- Complex Electrical Faults: Modern vehicles have intricate electrical systems, and issues like faulty wiring, damaged sensors, or malfunctioning control modules often require professional expertise to diagnose and repair. If you suspect an electrical problem is causing your parking brake light to stay on, it’s best to have a mechanic investigate.
- ABS Issues: If your vehicle’s ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) warning light is also illuminated along with the parking brake light, it could indicate a more serious problem within the braking system. ABS issues can significantly impact your vehicle’s safety and should always be addressed by a professional.
- Brake Fluid Leaks: If you notice brake fluid leaking from your vehicle or experience a soft, spongy brake pedal, it’s crucial to have a mechanic inspect your braking system immediately. If left unchecked, brake fluid leaks can lead to reduced braking performance and even complete brake failure.
- Unfamiliar or Complex Repairs: If the necessary repairs to address your parking brake light issue are beyond your skill level or require specialized tools, leaving the work to a professional is safer and more efficient. Attempting complex repairs without the proper knowledge or equipment can lead to further damage and potentially compromise your vehicle’s safety.
Regular Maintenance Tips
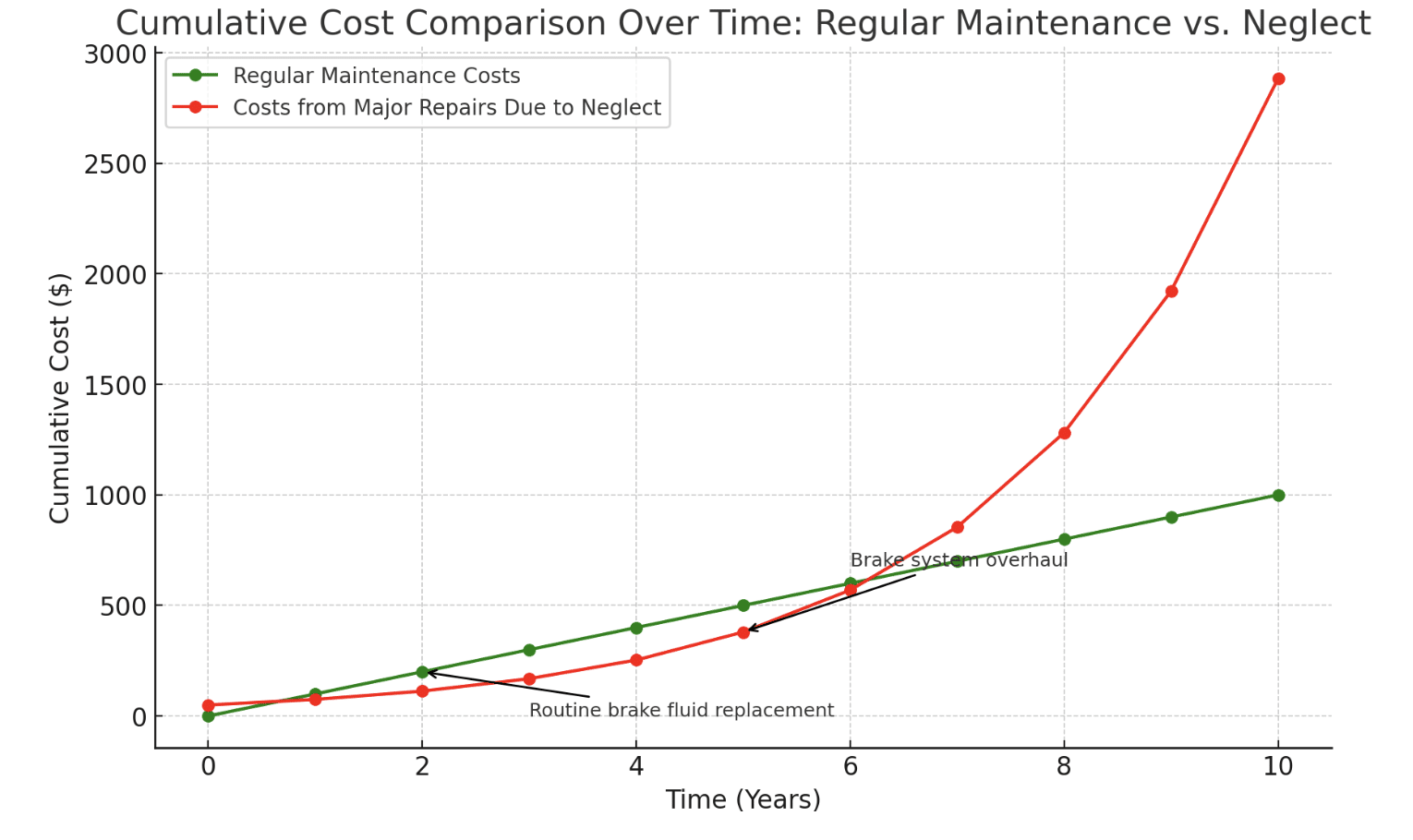
1. Checking Brake Fluid Levels
- Frequency and Process: Check your brake fluid levels at least once a month or as your vehicle’s manufacturer recommends. To check the fluid, locate the brake fluid reservoir under the hood and ensure that the level falls between the minimum and maximum marks on the side of the reservoir.
- Importance of Correct Fluid Levels: Maintaining proper brake fluid levels ensures adequate hydraulic pressure in the braking system. Low fluid levels can lead to reduced braking power and increased stopping distances.
2. Regular Inspections of Brake Pads and Sensors
- Scheduling Inspections: Have your brake pads and sensors inspected by a professional mechanic at least once a year or every 12,000 miles (19,000 km), whichever comes first. If you frequently drive in stop-and-go traffic or hilly areas, you may need to schedule inspections more often.
- What to Inspect: During the inspection, the mechanic will assess the thickness of your brake pads, ensuring they have not worn down beyond the recommended level. They will also check the condition of the brake sensors, looking for any damage or malfunctions that could cause the parking brake light to stay on.
Importance of Regular Service
1. Preventing Parking Brake Light Issues
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Brake Fluid Check | Every 3 months or 3,000 miles (4,800 km) | Check fluid level and top off if necessary. Look for signs of leakage. |
| Brake Fluid Replacement | Every 2 years or 24,000 miles (38,600 km) | Replace old fluid with new to prevent water contamination and corrosion. |
| Brake Pad Inspection | Every 6 months or 6,000 miles (9,600 km) | Check pad thickness and wear patterns. Replace if the thickness is below the manufacturer’s recommendation. |
| Brake System Inspection | Annually or 12,000 miles (19,300 km) | Comprehensive inspection of brake pads, rotors, drums, and lines. |
| Brake Line Inspection | Every 2 years or 24,000 miles (38,600 km) | Check for signs of wear, rust, and leakage. |
| Rotor Inspection | With every brake pad inspection | Check for warping or excessive wear, and resurface or replace as needed. |
2. Long-Term Benefits of Keeping Your Braking System in Optimal Condition
- Safety: A well-maintained braking system is essential for your vehicle’s safety. By ensuring your brakes function properly, you can react quickly and effectively in emergencies, potentially avoiding accidents and protecting yourself, your passengers, and other road users.
- Cost Savings: Preventative maintenance can save you money in the long run by identifying and addressing minor issues before they become more serious and expensive problems. By catching brake-related issues early, you can avoid costly repairs and extend the life of your brake components.
Wrapping Up
Dealing with a persistent parking brake light can be frustrating.
Still, by following the step-by-step troubleshooting guide in this article, you can quickly and safely identify and resolve the issue.
Remember to start with the basics, like ensuring the parking brake is fully disengaged and checking the brake fluid levels, before moving on to more complex fixes.
Regular maintenance, such as inspecting brake pads and sensors, can prevent future problems and keep your vehicle’s braking system in optimal condition.
If you’re unsure about any aspect of the troubleshooting process or encounter a complex issue, don’t hesitate to seek professional help from a qualified mechanic.
Taking a proactive approach to your vehicle’s maintenance can ensure a safer and more reliable driving experience for years.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is My Parking Light Blinking?
A blinking parking light usually indicates an issue with the parking brake system, such as a faulty switch, low brake fluid, or a problem with the brake mechanism itself.
What Causes a Parking Brake Malfunction?
Common causes of parking brake malfunctions include worn or misaligned brake pads, damaged cables, low brake fluid levels, or electrical issues affecting the brake switch or sensors.

