18-wheel trucks are a common sight on highways and roads, but do you know what makes them so important? These big trucks play a major role in transporting goods across long distances, keeping our economy moving.
In this guide, I will explain 18-wheel trucks, how they work, and why they are essential for getting products to stores and homes.
From their large size to powerful engines, 18-wheel trucks are built to handle heavy loads and travel across the country.
By the end of this blog, you will have a better understanding of these trucks and their importance in everyday life. Let’s learn more about the world of 18-wheel trucks.
What Is an 18-Wheel Truck?
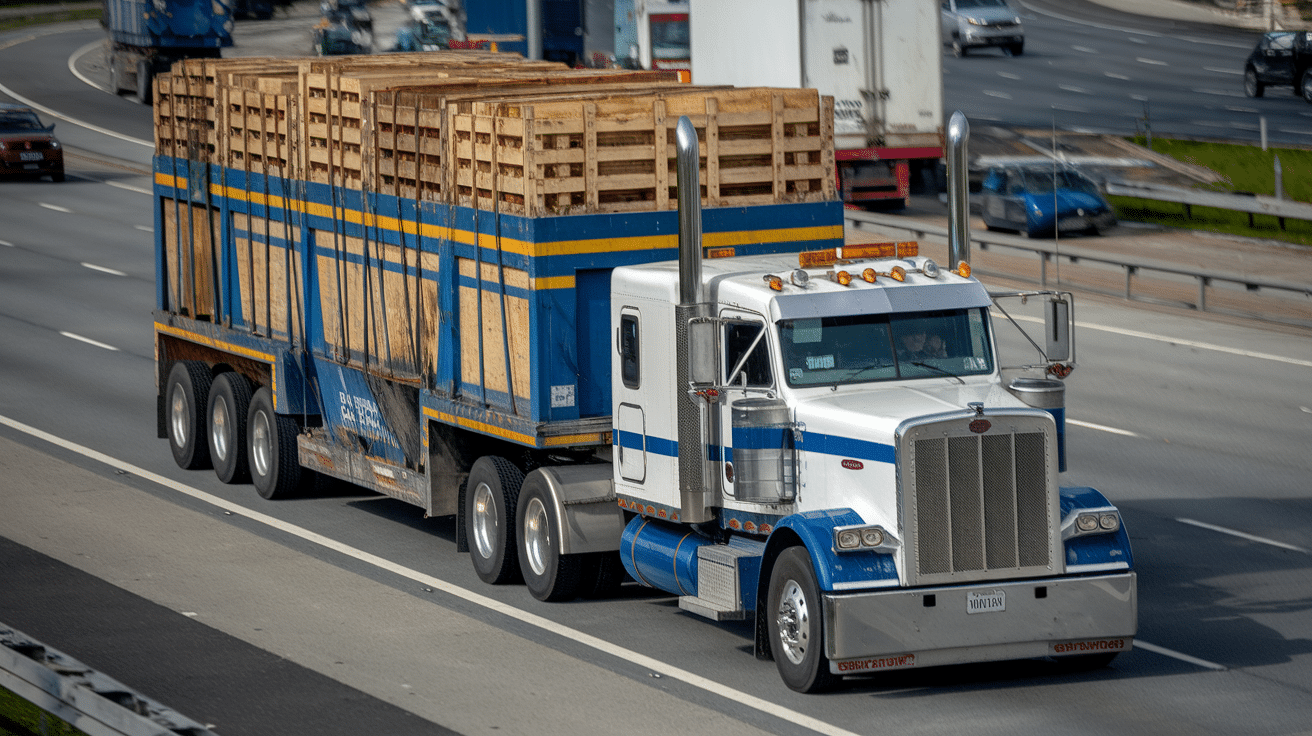

An 18-wheel truck, commonly known as a semi-truck, big rig, or tractor-trailer, is a large motor vehicle that transports goods over long distances.
It gets its name from the 18 wheels it uses to move and support its heavy load. These trucks are built to carry large quantities of cargo, often weighing thousands of pounds, and are a key component in the supply chain that helps move products across the country.
An 18-wheel truck has two main parts: the tractor (the front part) and the trailer (the back part).
- The Tractor: The tractor is the front section of the truck and contains the engine, driver’s cab, and other essential systems that allow the truck to operate. This part is essentially the “power unit” of the truck and is designed to pull the trailer.
- The Trailer: The trailer is the back part of the 18-wheel truck and is where the cargo is carried. The trailer is connected to the tractor by a coupling system, allowing it to pivot as the truck turns.
How It All Works Together
A fifth-wheel coupling system connects the tractor and trailer. This system is mounted on the back of the tractor and allows the trailer to pivot, making it easier for the driver to maneuver the truck, especially when making sharp turns or backing up.
The coupling ensures the trailer stays attached to the tractor during the journey, even under heavy loads. In terms of operation, the tractor’s engine provides power to the wheels, allowing the truck to move.
The driver controls the truck by shifting gears (in manual trucks) or using the automatic transmission to adjust speed and acceleration. The driver also uses a powerful brake system, typically air brakes, to slow down and stop the truck when necessary.
Size and Capacity
The size of an 18-wheel truck can vary, but typically, the total length from the front of the tractor to the end of the trailer is around 70 to 80 feet.
The weight limit for an 18-wheel truck can also vary, but in the U.S., the standard weight limit for a fully loaded truck is around 80,000 pounds.
The Importance of 18-Wheel Trucks
18-wheel trucks are the backbone of freight transportation. They are responsible for moving goods like food, clothing, electronics, and other products across the country.
Without these trucks, getting products from factories to stores or homes would be much harder.
These trucks travel on highways and roads, carrying goods for businesses and consumers. They help supply products to stores, making sure you can buy what you need.
In fact, 18-wheel trucks move about 70% of all freight in the U.S. That’s why they are often called “the lifeblood of the economy.”
The Parts of an 18-Wheel Truck
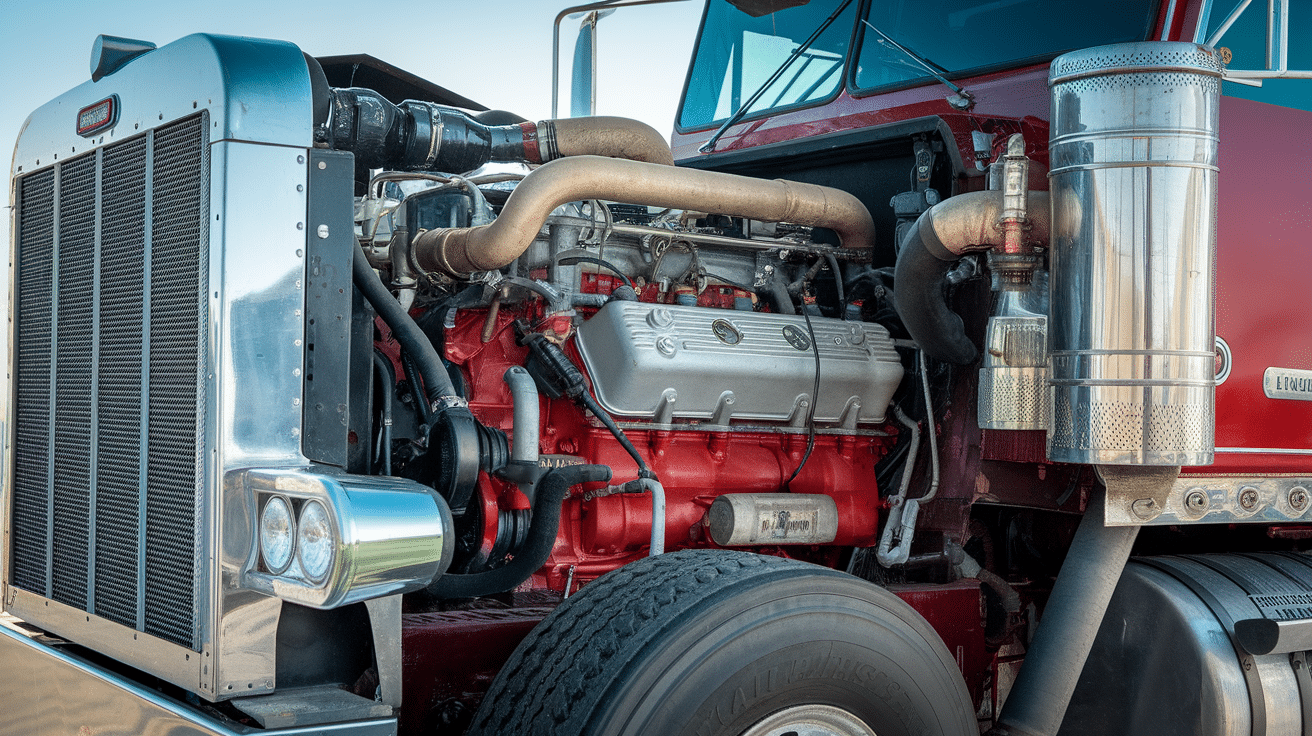
An 18-wheel truck comprises several key parts that work together to get the job done.
1. The Engine
The engine is the heart of the truck. It provides the power needed to move the truck and carry heavy loads.
Modern truck engines are powerful and efficient, designed to handle long-distance travel and heavy cargo. These engines can run for hundreds of thousands of miles before needing major repairs.
2. The Cab
The cab is where the driver sits and controls the truck. It’s designed for comfort since drivers often spend many hours on the road.
The cab has a seat, steering wheel, dashboard with controls, and sometimes a bed for the driver to sleep in. Some cabs even have kitchens and other amenities for long trips.
3. The Tires
An 18-wheel truck has a lot of tires—18 in total! These tires are large and strong to support the heavy weight of the truck and its cargo.
They are designed to handle long trips on highways, but they also need to be durable enough for rough roads and weather conditions.
4. The Trailer
The trailer is the part of the truck that carries the cargo. It is connected to the tractor with a fifth-wheel hitch, which allows the trailer to pivot and turn.
There are different types of trailers, including flatbeds, refrigerated trailers (for perishable goods), and dry vans (for general cargo).
5. The Brake System
The brake system is crucial for the safety of the truck and everyone on the road. It includes the air brakes, which use compressed air to slow down and stop the truck.
This system is much stronger than regular car brakes, allowing the truck to stop safely even when carrying heavy loads.
6. The Suspension
The suspension system helps smooth out the ride, especially when driving over rough roads. It keeps the truck stable and helps protect the cargo from damage.
This system uses springs, shocks, and other components to absorb bumps and jolts.
7. The Lights and Signals
The lights and signals are vital for driving safely at night or in poor weather. These include headlights, brake lights, turn signals, and hazard lights. They make sure other drivers can see the truck and know what it is doing.
8. The Coupling System
The coupling system connects the tractor to the trailer. It includes the fifth wheel, which locks into place to hold the trailer securely. This system is designed to be strong and durable, ensuring the trailer stays attached even under heavy loads.
Types of 18-Wheel Trucks

There are several types of 18-wheel trucks, each designed for different purposes.
- Flatbed Trucks: Flatbed trucks have an open, flat surface for loading cargo. They are commonly used to carry large, heavy items that don’t need protection from the weather, like construction materials, machinery, and large equipment. The cargo is secured with straps or chains.
- Refrigerated Trucks: Also known as reefer trucks, refrigerated trucks transport perishable goods such as food and medical supplies. They have cooling systems that keep the cargo at the right temperature throughout the journey, and the trailer is insulated to prevent temperature changes.
- Dry Van Trucks: Dry van trucks are the most common type of 18-wheel truck. These trucks have an enclosed trailer, protecting goods from the elements. They are used to transport a wide range of products, including electronics, clothing, and furniture.
- Tanker Trucks: Tanker trucks are designed to carry liquids such as fuel, water, chemicals, or milk. The tanks are built to hold large quantities of liquid and prevent leaks. These trucks have special safety features to ensure the liquid is securely transported.
- Car Carrier Trucks: Car carrier trucks are used to transport vehicles. They are specially designed to carry cars, trucks, or motorcycles from one place to another. These trucks have ramps and special loading features to load and unload vehicles safely.
- Logging Trucks: Logging trucks are designed to carry logs from forests to sawmills or other processing plants. These trucks often have specialized trailers and equipment to handle large, heavy loads of wood.
Each type of truck serves a specific purpose, but all of them play a vital role in the economy by transporting goods across long distances.
How 18-Wheel Trucks Work
18-wheel trucks are complex machines that rely on many different systems to work together. How they operate:
Starting the Engine
To get an 18-wheel truck moving, the driver starts the engine. The engine uses fuel (usually diesel) to create power.
This power is sent to the wheels through the truck’s transmission and driveshaft. The engine also helps power other systems, like the air brakes and the lights.
Driving the Truck
Once the engine is running, the driver shifts gears to control the truck’s speed. 18-wheel trucks have manual or automatic transmissions.
The driver uses the steering wheel to turn the truck and follow the road. The large size of the truck means that the driver needs to be careful, especially when turning or changing lanes.
Stopping the Truck
When the driver needs to stop, the brake system kicks in. Most 18-wheel trucks use air brakes, which are much stronger than regular car brakes.
These brakes are connected to a series of pipes that use compressed air to slow the truck down. The driver applies the brakes by pressing the brake pedal.
Turning and Maneuvering
Turning an 18-wheel truck can be tricky because of its size. The driver must be aware of the truck’s turning radius, which is how wide the truck needs to turn.
The driver uses mirrors and sometimes cameras to help them see around the truck and avoid obstacles.
Safety and Regulations for 18-Wheel Trucks

Since 18-wheel trucks carry heavy loads and travel long distances, safety is a top priority. Some of the safety rules and regulations that truck drivers must follow:
1. Weight Limits: There are strict rules about how much weight an 18-wheel truck can carry. These limits help prevent damage to roads and bridges and ensure that trucks can handle their loads safely.
2. Hours of Service: Truck drivers are required to follow strict rules about how many hours they can drive each day. This is to prevent driver fatigue, which can lead to accidents. Drivers must take regular breaks and rest periods.
3. Inspection and Maintenance: 18-wheel trucks must be regularly inspected and maintained to make sure they are in good working condition. This includes checking the brakes, tires, lights, and other important systems.
4. Safety Training: Truck drivers must complete safety training to ensure they know how to operate their trucks safely. They also need to be familiar with traffic laws and regulations.
The Role of 18-Wheel Trucks in the Economy
18-wheel trucks are vital for the economy because they transport most of the goods we use daily. Without them, stores would not have the products we need.
Moving Goods
18-wheel trucks transport goods from manufacturers to warehouses, distribution centers, and retail stores.
They can carry all kinds of products, from food and clothes to electronics and raw materials. This keeps stores stocked and ready for customers.
Job Creation
The trucking industry provides jobs for millions of people. These jobs include truck drivers, mechanics, logistics workers, and people who work at shipping and receiving facilities.
Truck drivers, in particular, have an important job, as they are the ones who drive the trucks long distances to deliver goods.
Supporting Other Industries
Many industries rely on 18-wheel trucks to deliver materials. Construction companies, for example, depend on trucks to transport building materials like wood, concrete, and steel.
The farming industry also relies on trucks to deliver fresh produce to stores.
Boosting Local Economies
When 18-wheel trucks deliver goods to stores and businesses, they help boost local economies.
Businesses use these goods to sell to customers, and their employees earn money. This money is then spent in local communities, helping businesses grow and creating even more jobs.
Conclusion
18-wheel trucks are essential for transporting goods across the country. They are built to carry heavy loads and travel long distances, making them a key part of our daily lives.
These trucks help keep stores stocked with products, support many industries, and play a vital role in the economy.
Over time, 18-wheel trucks have evolved to become safer, more efficient, and better for the environment. Truck drivers, too, have an important job in ensuring these trucks operate safely and efficiently on the road.
Without 18-wheel trucks, goods delivery would be much harder, and our economy would face many challenges. These trucks truly are the backbone of our transportation system.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the average fuel efficiency of an 18-wheel truck?
On average, an 18-wheel truck gets about 6 to 8 miles per gallon. However, fuel efficiency can vary based on the truck’s weight, speed, and driving conditions.
What are the most common types of cargo carried by 18-wheel trucks?
18-wheel trucks transport a wide range of goods, including food, building materials, electronics, chemicals, and furniture. The type of truck and trailer used depends on the cargo being transported.
How much does it cost to maintain an 18-wheel truck?
Maintenance costs can vary but typically range from $15,000 to $20,000 per year for a well-maintained truck. This includes regular inspections, repairs, and tire replacements.
How long do 18-wheel trucks last?
18-wheel trucks can last for hundreds of thousands of miles if properly maintained. With regular maintenance and repairs, some trucks can stay in service for 15 years or more.

