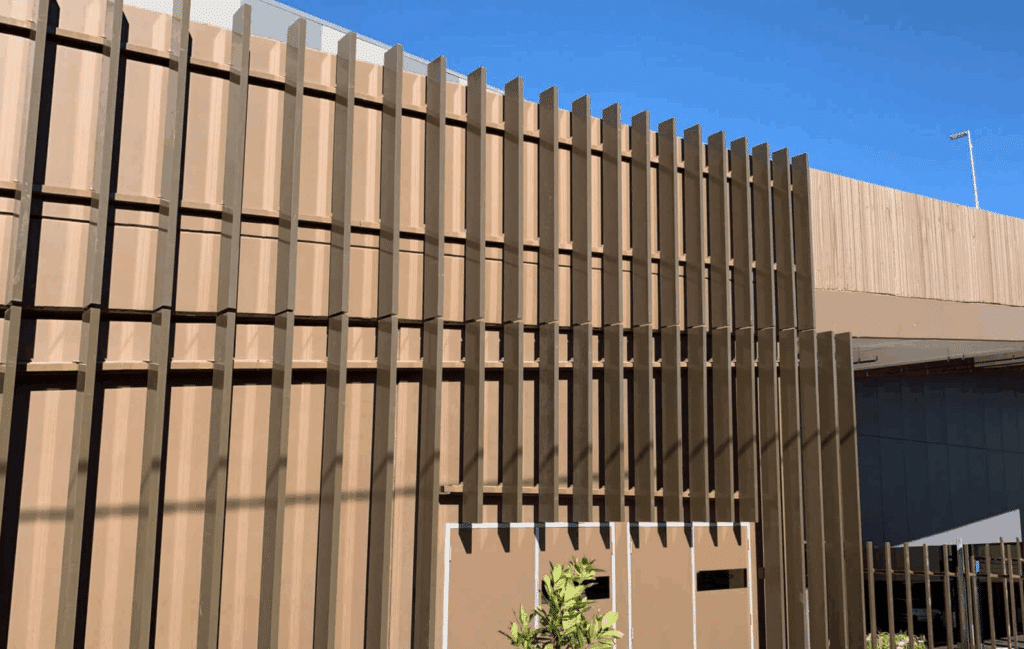
Modern architecture is increasingly requiring façades to balance functional performance with visual engagement. Aluminium façade blade systems have emerged as a solution that enables architects to create linear, textured, and durable exteriors while meeting the structural and environmental demands of contemporary building projects.
These systems make provision for design flexibility, streamlined installation processes, and durability in the long term; thus, they can be applied on a wide range of architectural applications. This article explores the technical characteristics, design considerations, and practical implementation aspects of aluminium façade blade systems that can be useful to architects and specifiers seeking to understand their potential and application requirements.
Facade Blades
Façade blades are extruded aluminium profiles engineered for external wall applications where designers want to achieve a sculptural, linear façade treatment. Unlike traditional cladding systems with their continuous panels or small-scale components, blade systems take advantage of the use of elongated profiles mounted to a structural rail framework.
This approach provides linear patterns that are distinctive and three-dimensional surface effects responding dynamically to the daily changes in lighting.
The system’s fundamental construction methodology consists of a mounting rail system fixed to the primary or secondary building structure. These rails establish the structural support framework and determine the overall geometry of the façade surface.
Individual blade profiles, prefinished from the manufacturer, are then attached to the rails at predetermined locations using clips or brackets. This modular installation approach creates a streamlined construction sequence that reduces site complexity and accelerates project timelines.
The blade profiles themselves are precision-extruded aluminium sections available in a variety of depths and widths to suit various aesthetic intentions and structural requirements. The profiles include mounting features as part of their geometry for secure attachment to the rail system while maintaining clean visual lines without visible fasteners on the façade face. This concealed fixing methodology contributes to the refined appearance characteristic of well-executed blade façade systems.
Products such as Facade blades represent this approach by offering engineered systems developed for large-scale external applications where long spans, consistent alignment, and simplified installation are among the project priorities. These systems are engineered to address the structural, weatherproofing, and aesthetic requirements that define successful contemporary façade construction.
Structural and Design Considerations
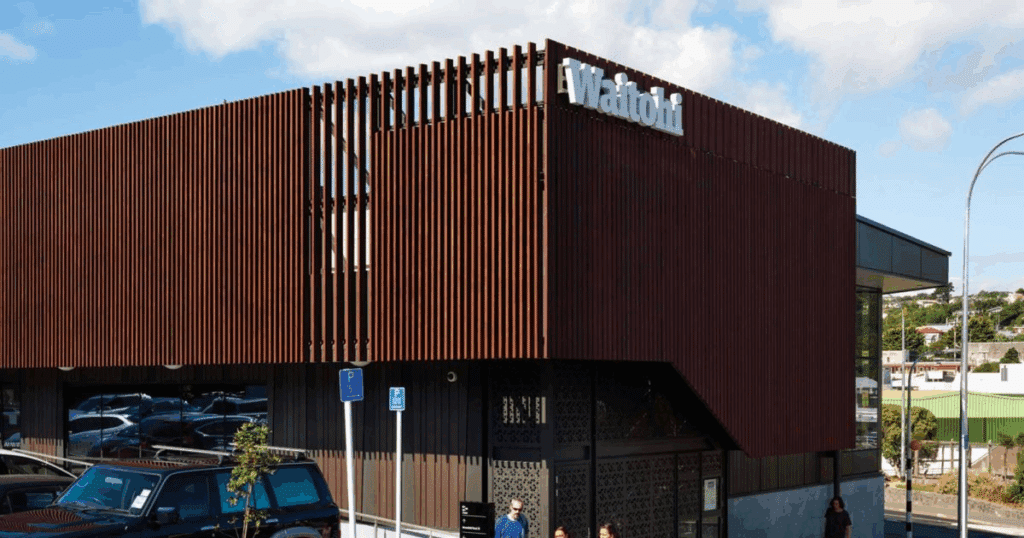

Specification and application of aluminum façade blade systems in architectural projects are influenced by several technical factors.
Span Capabilities and Structural Performance
A major advantage of aluminium blade systems is their ability to span large distances between support points. This is a desired feature, as it enables designers to create large façade surfaces with minimal visible supporting structure, providing clean, continuous lines-of-sight. The achievable span depends on many factors, such as blade profile depth, material thickness, wind loading, and installation orientation.
Greater structural capacity and longer unsupported spans naturally come with deeper blade profiles. Under normal load conditions, blades nearing the three hundred millimeter depth can span several meters between mounting rails; however, project specifics must be verified through engineering. In each application, the relationship between blade depth, span length, and expected loads must be assessed to ensure that structural adequacy throughout a building’s service life is achieved.
Wind loading is the most important structural consideration related to the use of blades as an exterior façade. Design wind pressures are highly variable, depending on building height, surrounding terrain, geographic location, and local climatology. Blade systems are required to resist positive pressure-which pushes inward-and negative pressure-suction pulling outward-without excessive deflection or failure of the fixing system. Engineering analysis calculates these forces and verifies that the blade profile specified, along with spacing of mounting rails and fixing details, will safely support those forces with appropriate safety factors.
Geometric Flexibility and Complex Forms
Contemporary architecture often involves curved or angled, or non-orthogonal building forms that create challenges for traditional cladding systems. Aluminium blade systems can accommodate these complex geometries in a number of ways. Curved mounting rails follow the intended geometry in the façade and provide the three-dimensional framework to which straight blade profiles are attached. Individual blades remain straight, while their assembly on curved rails presents an overall curved surface appearance.
Adjustable mounting brackets provide angular variation at each fixing point, allowing blades to follow raked surfaces, transition between planes, or create faceted effects. This adjustability is highly valuable in the retrofit of façades to existing structures where perfect alignment may be challenging, or when the design brief involves intentionally dynamic surface geometries that shift across the building elevation.
The combination of curved rails and adjustable brackets extends design possibilities beyond simple planar applications, making blade systems suitable for sculptural building forms, curved corner conditions, and architecturally expressive façade treatments. This geometric capability allows consistent material vocabulary across both conventional and complex building surfaces within a single project.
Installation Methodology and Site Efficiency
It provides several practical advantages during construction. In the rail-and-blade installation approach, the mounting rail framework installs first, establishing the structural support system and the overall geometry of the façade. Measurement, careful alignment, and fixing will be done at this initial phase so that the finished façade achieves intended dimensions and performance characteristics. Rails attach to the building structure through brackets allowing for construction tolerances and providing adjustment capability.
Once the rail system has been verified and secured, blade installation proceeds as a fairly straightforward process. Prefinished blades arrive on site ready for installation, avoiding field finishing operations that could compromise quality or introduce project delays. Each blade clips or slots into the rail system at predetermined locations, thereby automatically creating consistent spacing and alignment. This modular approach reduces installation complexity, minimizes the skill level required for field labor, and accelerates construction progress.
The hidden fixing methodology presents clean visual lines with no fastener heads visible on the finished façade. This adds not only to aesthetic refinement but also eliminates potential points of water penetration associated with face-fixed systems. Since the system is modular, it allows for future maintenance or replacement of individual components without affecting other adjacent elements, thus supporting long-term serviceability of the building.
Material Characteristics and Finish Options
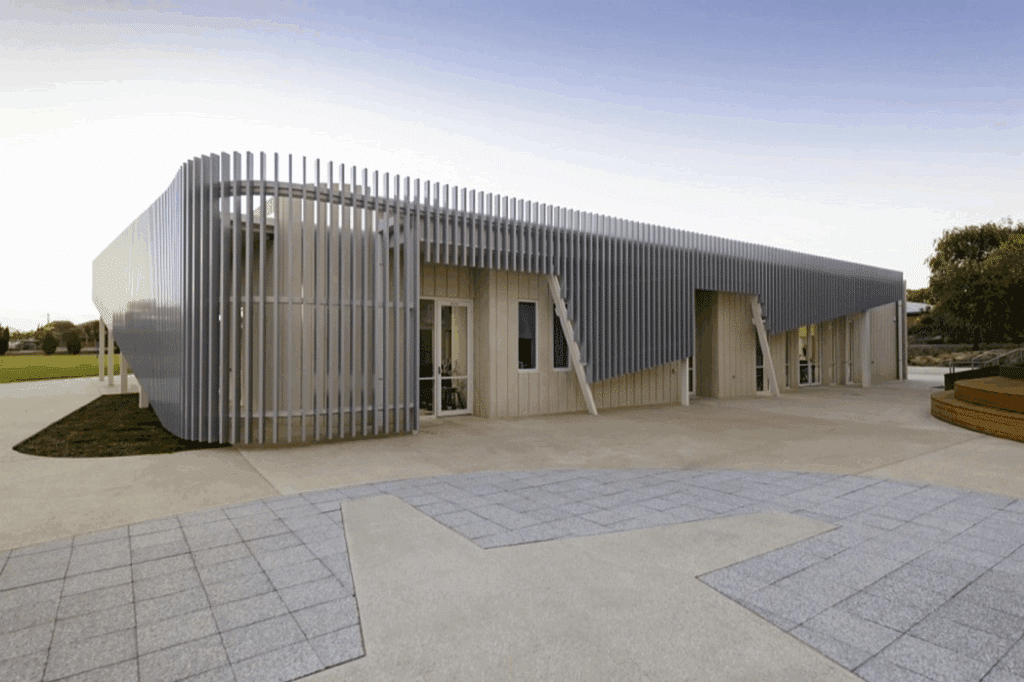

The selection of aluminum alloys used in facade blade systems balances tensile strength, durability, corrosion resistance, and workability. These are achieved with common alloys that include compositions within the six thousand series. These offer a good mix of properties: structural properties, excellent extrusion characteristics, and effective surface treatment compatibility. The alloys maintain dimensional stability across wide temperature ranges and resist degradation from environmental exposure over an extended service life.
Standard blade profiles come in many dimensional configurations to meet various design intentions and structural requirements. Some common dimensions include profiles fifty millimeters wide combined with depths of one hundred fifty millimeters, two hundred millimeters, or three hundred millimeters.
These options for dimensions enable a designer to select an appropriate profile given the span required, the intended visual depth, and shadow effects. Special geometries can be developed for custom projects that have unique aesthetic or technical needs; however, these usually are more expensive and take longer to produce than standard profiles.
Selection of surface finish significantly influences appearance and long-term performance. Several finish categories are commonly specified for exterior blade applications. Powder-coated finishes apply durable polymer coatings through electrostatic application and heat curing processes.
These finishes provide excellent color consistency, ultraviolet resistance, and weather durability. An extensive color range allows coordination with broader project palettes; various texture options are also available, from smooth to textured surfaces, offering additional aesthetic variation.
Anodized finishes are electrochemically applied on the aluminum surface to create a protective oxide layer. These finishes offer metallic appearances with great resistance to corrosion and durability. Natural anodized finishes reveal the underlying characteristics of metals, while color anodizing introduces subtle tones. Anodized finishes will maintain their appearance for decades without significant maintenance.
Timber-look wrapped finishes provide a realistic wood grain pattern and texture to aluminium substrates through film application technologies. These finishes allow designers to achieve timber aesthetics while retaining the structural, fire performance, and maintenance advantages of aluminium.
The films are engineered for exterior exposure, with ultraviolet stability and weather resistance, though long-term appearance retention should be evaluated based on specific exposure conditions and project expectations.
Applications in Different Building Categories
Aluminum façade blade systems suit a wide range of building types and architectural contexts where durable, visually engaging exterior treatments are required.
Blade façades in commercial office buildings are commonly used to achieve specific architectural identities and, at the same time, fulfill certain performance criteria in terms of weather protection and thermal efficiency with their backing systems. The linear nature of blade systems fits well in most modern commercial architecture and can be designed to achieve solar shading benefits when correctly oriented and spaced.
Educational facilities benefit from the durability and low maintenance characteristics of blade systems, in addition to aligning well with the typical institutional budget constraints and operational priorities. Visual interest through blade façades further creates engaging learning environments, while robust construction can withstand the extended service lives expected for educational buildings.
Blade systems are specified in healthcare projects for their clean appearance, ease of cleaning, and their ability to create calming visual environments through controlled linear patterns and shadow effects. The hygienic properties of the material and resistance to biological growth support healthcare facility requirements.
Blade façades are used in transport infrastructure, such as rail stations, airports, and transit centers, due to their ability to efficiently cover large surface areas while creating architectural distinction for public buildings. The system’s capacity for complex geometries accommodates the often non-orthogonal forms characteristic of transport architecture.
Multi-residential developments use blade systems to differentiate projects in competitive markets while controlling construction costs through efficient installation. Visual interest and architectural character are provided by façade treatment, which enhances perceived value without resorting to complicated construction processes or extended schedules.
Visual Effects and Design Variables
The visual character of an aluminium blade façade arises from the amalgamation of several controllable design variables that architects manipulate to produce intended aesthetic outcomes.
Blade depth has a direct relationship with the intensity of shadow and three-dimensional relief. Deeper profiles produce stronger shadow effects that may be used to reinforce the linearity of the façade. Shallower profiles can be used in applications where a more subdued expression is desired. The relationship between the depth of the blade and viewing distance is important, as very shallow profiles may appear flat from a typical view position.
Spacing between the adjacent blades controls the visual density, transparency, and amount of substrate concealment behind the blade system. Tight spacing generates relatively opaque surfaces with restricted views through the façade, whereas wider spacing increases transparency and can reveal the backing material. Spacing usually ranges between one hundred millimeters and three hundred millimeters, although applications may provide justification for using spacing wider or narrower than this range. The selection of spacing shall take into consideration functional requirements such as privacy, solar control, and ventilation together with the aesthetic intention.
The angle at which the blades are oriented significantly affects the visual character as well as functional performance. Vertical blades emphasize building height and create strong vertical rhythms. Horizontal blades reinforce floor lines and building proportions by providing solar shading for correctly oriented façades. Diagonal orientations introduce dynamic visual movement that could respond to specific site conditions or design concepts. Variation in orientation within a single façade creates visual complexity and hierarchy.
Dynamic surface effects are developed through the interplay of natural light and blade geometry, shifting throughout the day according to sun angles. Morning and evening lights at low angles generate dramatic shadow patterns, whereas midday light might lower contrast. Such effects can be studied in more detail by designers using various digital modeling or physical mockups to optimize blade configuration for desired visual outcomes at site-specific conditions.
Engineering and Installation Considerations
The implementation of aluminum blade façades is successful if multiple technical factors are taken into consideration during the design and construction process.
Structural Engineering Input
Blade system specifications should be reviewed for structural adequacy by qualified structural or façade engineers under project-specific conditions. This review includes wind load calculations based on building height, exposure category, and local design wind speeds. This analysis confirms that the specified blade profiles, rail spacing, and fixing details can safely resist calculated loads with appropriate safety factors. Wind tunnel testing or computational fluid dynamics analysis may be required to establish accurate design pressures for tall buildings or exposed sites.
The structure of the mounting rail system must be analyzed for capacity verification under transferred loads from the blades. Rails must safely span between support brackets without excessive deflection, and bracket fixing to the primary structure must develop adequate strength. The cumulative loads transferred to the building structure should be verified to be within the capacity of the supporting elements.
Blade Spacing and Alignment
Precise blade spacing and alignment is critical to achieve intended visual effects and ensure consistent appearance. Spacing is an aesthetic concern, but it also affects the structural performance. Closer spacing can increase wind loads due to reduced venting. Installation tolerances should be established and maintained to prevent visible irregularities in the finished façade.
The mounting rail system establishes the principal alignment framework. Rails must be positioned accurately in three dimensions, since errors in rail location translate directly to blade position discrepancies. Quality control during rail installation prevents compounding errors that become apparent once blades are installed.
Final Selection Based on Environmental Conditions
Appropriate finish selection is also influenced by the service environment: In coastal locations with salt exposure, finishes must be selected that have demonstrated corrosion resistance along with regular maintenance protocols to remove the salt deposits. Finishes for high ultraviolet exposure such as tropical or high-altitude locations must have documented ultraviolet stability to avoid premature fading or chalking. Areas with industrial atmospheric pollutants may necessitate a higher cleaning frequency.
Wrapped finishes that mimic the look of timber are aesthetically pleasing but their long-term weathering performance should be considered with respect to exposure severity and maintenance commitment.
These finishes are engineered for exterior use, although their appearance retention over decades should be considered in light of project expectations and maintenance capabilities. Maintenance Requirements Aluminum blade systems are inherently low maintenance compared to many alternative façade materials.
The material does not rot, rust, or require refinishing under normal conditions. However, periodic maintenance supports long-term appearance and performance. Regular inspection identifies potential issues before they develop into significant problems.
Gentle cleaning with water or soft brushes removes accumulated dirt, pollutants, and biological growth. Harsh cleaning methods or abrasive materials should be avoided as they may damage surface finishes. The modular nature of blade systems accommodates the replacement of components when damage has occurred or maintenance is needed. Individual blades can usually be removed and replaced individually, without affecting adjacent elements, thereby supporting long-term building serviceability and appearance maintenance.
Aluminium façade blade systems provide architects with a versatile tool for creating visually engaging, structurally sound, and durable building exteriors. In fact, long-span capability, geometric flexibility, streamlined installation, and low maintenance requirements make such systems suitable for a wide range of project types and different architectural intentions.
Knowledge of the technical characteristics, design variables, and implementation considerations empowers informed specification decisions that meet system capabilities to project requirements. For applications where clean linear aesthetics, modular construction efficiency, and long-term exterior performance are priorities, aluminium blade systems offer a practical and effective façade solution.