Wheel spacers are metal components placed between the wheel hub and the wheel. They push the wheels outward, giving the vehicle a wider stance. Many car owners use spacers to improve appearance, fit larger tires, or enhance stability.
Some drivers worry about how spacers affect safety and performance. Poor-quality or incorrectly installed spacers can lead to handling issues, vibrations, or added strain on suspension parts.
On the other hand, properly installed spacers made from strong materials can function safely without causing damage.
The key to using spacers safely depends on the material, fit, and correct installation.
Understanding their impact on a vehicle helps drivers decide if spacers are a good choice for their specific needs.
What Are Wheel Spacers?
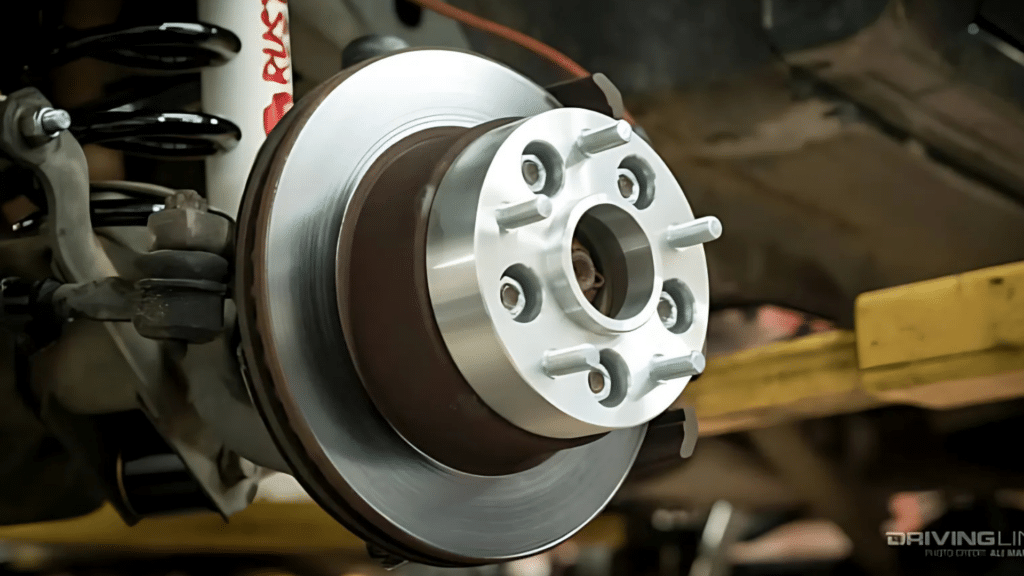
Wheel spacers are metal rings installed between the wheel hub and the wheel. They create extra space, pushing the wheels outward.
This changes the vehicle’s stance and can help with clearance issues when using aftermarket wheels or wider tires.
There are two main types of spacers: hub-centric and lug-centric. Hub-centric spacers are designed to fit perfectly onto the hub, ensuring even weight distribution and reducing vibrations.
Lug-centric spacers rely on the lug nuts to center the wheel, sometimes leading to alignment issues if not installed correctly.
When used properly, wheel spacers can improve handling by widening the vehicle’s track, enhancing stability, and helping with cornering performance.
However, choosing the right spacers is important to avoid issues with safety and durability.
Why Do People Use Wheel Spacers?
Many car owners use wheel spacers to achieve a more aggressive stance by pushing the wheels outward. This gives the vehicle a wider, sportier look.
Spacers also help when installing aftermarket wheels that might not fit correctly due to different offsets.
For performance drivers, spacers can improve handling by increasing track width. A wider stance enhances cornering ability and stability, especially in high-speed situations.
Off-road enthusiasts also use spacers to fit larger tires and improve ground clearance, making driving easier on rough terrain.
In some cases, spacers are necessary when upgrading brake systems.
Aftermarket brake kits can sometimes require extra space between the wheel and caliper, making spacers a practical solution for better fitment.
Types of Wheel Spacers
There are two main types of wheel spacers: bolt-on and slip-on.
- Bolt-on Spacers: These attach directly to the wheel hub with their own set of lug nuts. The wheel is then mounted onto the spacer using separate lug nuts. This design is more secure and is often used for larger spacers (10mm or more).
- Slip-on Spacers: These slide over the existing wheel studs and require longer lug bolts to secure the wheel. They are typically used for smaller spacing adjustments (3mm–10mm) and are more common for minor fitment corrections.
Spacers are also made from different materials, with the most common being billet aluminum and cast aluminum. Billet aluminum spacers are stronger and more durable as they are machined from solid metal.
On the other hand, cast aluminum spacers are made by pouring molten metal into a mold, which can create weak spots and reduce durability.
High-quality materials ensure that spacers can handle the stress of daily driving without failure.
The Risks of Using Wheel Spacers
Wheel spacers can affect a vehicle’s handling, affecting its suspension, alignment, and steering.
While some drivers use them for better fitment or performance, improper installation or low-quality spacers can lead to serious issues.
The added distance between the wheel and hub changes how weight is distributed, increasing stress on important components.
Not all spacers cause problems, but using the wrong type or failing to install them correctly may reduce the lifespan of suspension parts, affect stability, and create safety risks.
Understanding these potential downsides helps drivers make informed decisions before using spacers on their vehicles.
Increased Stress on Wheel Bearings and Suspension
Wheel spacers push the wheels farther from the hub, changing how force is applied to suspension and wheel bearings.
This increased leverage puts extra strain on these parts, leading to premature wear.
Over time, the added stress can cause wheel bearings to fail sooner than expected, resulting in costly repairs.
Due to the changed wheel position, suspension components, including ball joints and control arms, also experience greater pressure.
If the vehicle isn’t designed to handle this added strain, it may lead to uneven tire wear, alignment issues, and a rougher ride.
Changes in Steering and Handling
Adding spacers can affect how a vehicle steers and responds to road conditions.
By altering the scrub radius—the distance between the tire’s contact patch and the steering axis—spacers can make steering feel heavier or less predictable.
Spacers may sometimes improve cornering stability by widening the track width, but they can also cause instability at higher speeds.
If the spacers are too thick, they may reduce steering precision, making it harder to control the vehicle, especially during sudden movements or emergency braking.
Risk of Spacer Failure
The quality and installation of wheel spacers determine their safety. Poorly made spacers, or improper installation can lead to serious failures.
If spacers are not properly torqued, they may loosen over time, causing vibrations or even detachment of the wheels.
Material strength is another important factor. High-quality spacers made from strong materials like billet aluminum offer better durability, while low-quality cast aluminum spacers may crack under pressure.
Ensuring that spacers are properly installed, torqued to the correct specifications, and regularly inspected reduces the chances of failure.
Are Wheel Spacers Safe to Use?
Wheel spacers can be safe when chosen carefully, installed correctly, and maintained properly.
Many drivers use high-quality spacers to improve wheel fitment, enhance stability, or allow for larger brakes without experiencing problems.
However, poorly made spacers or incorrect installation can create serious risks.
The key to using spacers safely is selecting the right type, ensuring they are hub-centric, and following proper installation steps.
With the right approach, wheel spacers can provide benefits without affecting the vehicle’s handling or reliability.
Choosing the Right Spacer
Selecting the right spacers is essential for safety and performance.
Hub-centric spacers are recommended because they align perfectly with the vehicle’s hub, reducing the chance of vibrations or stress on the wheel studs.
Lug-centric spacers, which rely only on lug nuts for centering, can cause imbalance and should be avoided in most cases.
The thickness of the spacer must also be considered. Spacers that are too thick may push the wheels out too far, creating excessive stress on suspension components.
Choosing a size that maintains a proper balance between performance and safety is important.
Material quality plays a big role in spacer durability. High-quality billet aluminum spacers offer better strength and resistance to cracking or bending.
Cheaper cast aluminum spacers may be weaker and more likely to fail under pressure. Choosing a reputable brand with a history of reliable products helps ensure better results.
Proper Installation and Maintenance
Correct installation is critical to keeping wheel spacers safe. Spacers must be torqued to the manufacturer’s recommended settings to prevent loosening over time.
Under-tightened or over-tightened spacers can lead to wheel vibrations, uneven wear, or, in extreme cases, wheel detachment.
Thread engagement is another important factor. The wheel studs should have enough engagement to keep the wheel securely fastened.
Extended studs may be required for a secure fit if the stock studs are too short after adding spacers.
Regular inspection is also necessary. Checking the spacers for looseness, cracks, or signs of wear helps prevent potential failures.
If any issues appear, it’s best to remove or replace them before they damage the wheels or suspension.
By selecting high-quality spacers, installing them correctly, and inspecting them regularly, drivers can use wheel spacers safely without compromising their vehicle’s performance or reliability.
When Should You Avoid Wheel Spacers?
Wheel spacers can improve fitment and handling when used correctly, but they are not always the right choice.
In certain situations, using spacers may create safety risks, increase wear on vehicle components, or lead to handling issues. Below are cases where wheel spacers should be avoided.
Extreme Racing or High-Performance Driving
Vehicles used for high-speed racing or aggressive cornering should avoid wheel spacers unless professionally tested.
The added leverage on wheel bearings and suspension can increase wear and reduce stability at high speeds.
Racing applications require precise engineering, and improperly installed spacers can lead to unpredictable handling or failure under extreme loads.
Heavy Towing or Overloaded Vehicles
Trucks and SUVs used for towing large loads or carrying heavy cargo should avoid wheel spacers, as they increase stress on suspension and axles.
The extra leverage can accelerate wear on wheel hubs, bearings, and control arms, leading to potential failures.
Manufacturers design suspension and wheel positioning with load distribution in mind, and spacers can disrupt that balance.
Using Excessively Thick Spacers
Spacers over 20mm (0.8 inches) can push wheels too far outward, affecting handling and stability.
Thick spacers create additional strain on wheel studs and lugs, increasing the risk of failure.
If a vehicle requires spacers beyond safe limits, purchasing wheels with the correct offset may be better than relying on spacers.
Poorly Maintained Vehicles
If a vehicle already has worn-out suspension, damaged wheel bearings, or alignment issues, adding spacers can make these problems worse.
Spacers do not fix existing suspension problems and may cause uneven tire wear or vibrations.
Before installing spacers, ensure that the vehicle’s suspension and wheel components are in good condition.
Using Cheap or Low-Quality Spacers
Unbranded or poorly machined spacers may have weak materials, improper fitment, or structural flaws.
Cast aluminum spacers are more prone to cracking compared to high-quality billet aluminum options.
Always choose spacers from a reputable manufacturer to ensure proper safety and durability.
By avoiding wheel spacers in these situations, drivers can prevent unnecessary wear, improve safety, and maintain proper vehicle performance.
Conclusion
When used correctly, wheel spacers can improve a vehicle’s stance, handling, and fitment. They allow for better clearance, wider track width, and compatibility with aftermarket wheels.
When high-quality spacers are installed properly, they can enhance performance without major risks.
However, spacers also come with downsides. They can put extra stress on wheel bearings and suspension components.
If improperly installed or used in extreme conditions like heavy towing or racing, they may lead to instability or premature wear.
Always choose well-made spacers from trusted brands and follow correct installation practices to ensure safety.
Regular maintenance and inspections are key. If unsure about using spacers, consulting a professional can help determine if they are a good choice for your vehicle.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are Wheel Spacers Bad for My Car’s Suspension?
Wheel spacers put extra stress on suspension parts like wheel bearings and ball joints. Properly sized and high-quality spacers reduce these risks.
Do Wheel Spacers Affect Handling and Steering?
Yes, spacers can change the vehicle’s scrub radius, making steering feel heavier or less responsive. The impact depends on spacer thickness and alignment.
Can Wheel Spacers Cause Vibrations?
Improperly installed or low-quality spacers can cause vibrations. Hub-centric spacers help prevent this by ensuring a secure and balanced fit.
Are Wheel Spacers Safe for Daily Driving?
Yes, if installed correctly and checked regularly. Using high-quality spacers with proper torque settings helps maintain safety.
How Thick Should Wheel Spacers Be?
Spacer thickness depends on the vehicle and wheel setup. Excessive thickness can stress suspension parts and cause alignment issues.
Can I Use Wheel Spacers for Off-Roading?
Many off-road drivers use spacers to widen the track for better stability. However, strong, high-quality spacers are essential to handle rough terrain.

