Looking at a window might seem simple, but there’s more to it than meets the eye.
Most people don’t think twice about what makes a window work. They open it, close it, and that’s that. But each window is made up of several parts working together. Some keep the cold out. Others let light in. A few handle the opening and closing.
When something breaks or needs replacing, knowing the proper term helps. Plus, it makes choosing new windows much easier.
This post breaks down each essential part and explains what it does.
Evolution of Window Designs and Parts Over Time
Window construction has changed dramatically over the centuries. Early windows were simple openings with wooden shutters. Glass was rare and expensive, reserved for wealthy homes and churches.
As glassmaking improved, single-pane windows became common, though they offered little insulation.
The industrial revolution brought mass-produced components and standardized sizes. Double-hung windows dominated through the 1800s and early 1900s.
Counterweights and pulleys made the operation easier but created air leaks.
Modern windows emerged in the mid-1900s with insulated glass units and vinyl frames. Today’s designs prioritize energy efficiency, using low-E coatings, argon gas fills, and warm-edge spacers.
Hardware has evolved from simple latches to multi-point locking systems. Manufacturing precision has improved weatherstripping and sealing methods, making contemporary windows far more efficient than their predecessors.
Anatomy of All Window Components
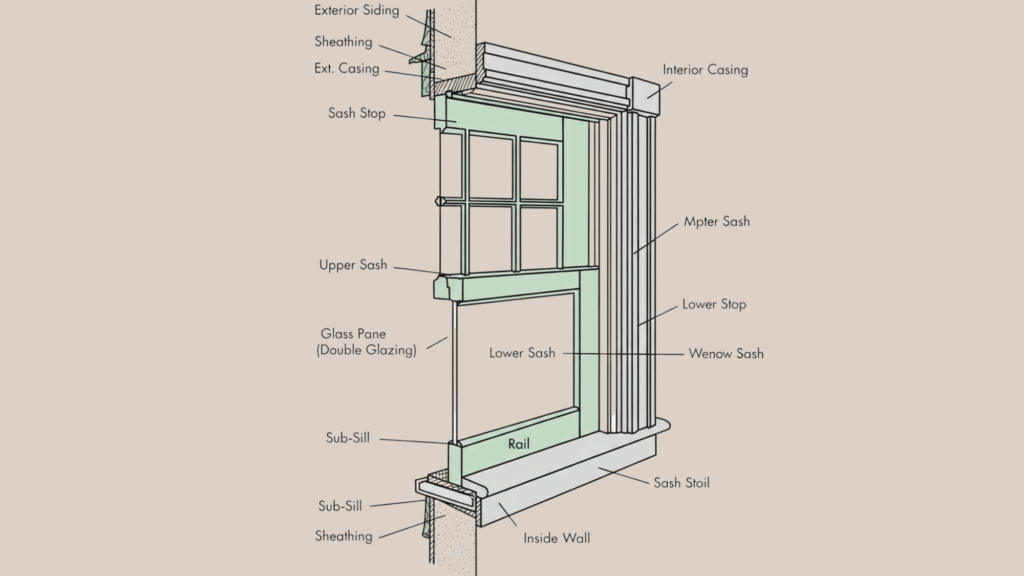
A window system combines structural framing, movable sashes, glazing, hardware, seals, and finishes. Each component works together to ensure strength, operation, insulation, weather resistance, and visual balance.
Frame Parts
The frame anchors the window to the building and provides the foundation for all other components.
1. Head Jamb
The head jamb is the top horizontal structural member of a window frame. It supports the load above the opening, maintains frame alignment, and helps transfer weight to the surrounding wall framing.
Properly installed head jambs prevent sagging, ensure smooth sash movement, and often integrate with flashing systems to reduce water intrusion from above.
2. Side Jambs
Side jambs are the vertical frame members positioned on the left and right sides of the window opening. They guide sash movement, house balance systems or tracks, and maintain the overall squareness of the window.
Accurate alignment of side jambs is essential for smooth operation, effective sealing, and long-term structural stability.
3. Sill
The sill is the bottom horizontal frame element, usually sloped outward to direct water away from the building. It supports the window assembly, prevents moisture infiltration, and channels water toward weep holes.
Durable sill construction is critical, as this area experiences the most exposure to rain, condensation, and temperature changes.
4. Jambliner
A jambliner is an interior lining fitted inside the side jambs, forming precise tracks for sash movement. It often houses balance mechanisms and provides a smooth, low-friction surface for sliding windows.
Jambliners also improve air sealing and allow for easier maintenance or sash removal in modern window systems.
Sash and Glass (Movable Glazing Holder)
The sash holds the glass and moves to allow ventilation and light control.
5. Sash
The sash is the movable framework that holds the glass within the window. In double-hung windows, there are upper and lower sashes that slide independently.
The sash allows ventilation, supports glazing, and interfaces with locks and balances. Precision construction ensures smooth movement, proper sealing, and long-term durability.
6. Top Rail
The top rail is the upper horizontal member of a window sash. It connects the two sills, stabilizes the sash structure, and provides a sealing surface when the window is closed.
In operable windows, the top rail plays a key role in maintaining alignment and ensuring a tight, weather-resistant closure.
7. Bottom Rail
The bottom rail is the lower horizontal component of the sash and often the most handled part.
It supports the weight of the sash, contributes to structural rigidity, and provides a grip area for lifting or closing. Its design must resist moisture exposure and repeated use without warping or deterioration.
8. Check Rail
The check rail is the meeting edge where the upper and lower sashes come together in double-hung windows. It forms a critical sealing point that prevents air and water infiltration when the window is closed.
Check rails often integrate locks and reinforcement to improve security and overall window performance.
9. Stiles
Stiles are the vertical sides of a sash that connect the top and bottom rails. They provide structural strength, house locking hardware, and guide the sash along jamb tracks.
In casement and awning windows, stiles are especially prominent, as they support hinges and operators while maintaining a tight perimeter seal.
10. Glass Pane / IGU
The glass pane, commonly configured as an insulated glass unit (IGU), consists of two or three panes separated by spacer bars and sealed with gas fills like argon.
IGUs improve thermal insulation, reduce noise, and enhance energy efficiency. Low-emissivity coatings further control heat transfer and UV penetration.
Window Hardware Essentials
These components enable smooth window operation while keeping air, water, and drafts out.
11. Balance/Spring
Balances or spring systems counteract the weight of the sash, allowing smooth and effortless opening and closing. They replace traditional counterweights in modern windows and are concealed within jamb liners or frames.
Properly calibrated balances reduce strain on hardware and improve usability over the window’s lifespan.
12. Sash Lock
A sash lock secures the window in a closed position, improving safety, security, and weather sealing. Located at the meeting rails, it pulls the sashes tightly together when engaged.
High-quality sash locks also help reduce air leakage by ensuring consistent compression of weatherstripping along contact points.
13. Crank / Operator
Cranks or operators are mechanical devices used in casement and awning windows to open and close the sash. They convert rotational motion into controlled sash movement, allowing precise ventilation adjustments.
Operators also help maintain tight sealing when closed by pulling the sash firmly against the frame.
14. Weatherstripping
Weatherstripping consists of flexible materials installed along sash and frame edges to seal gaps. It prevents drafts, reduces energy loss, and blocks water and dust infiltration.
Effective weatherstripping compresses evenly during closure and rebounds after use, maintaining insulation performance despite repeated window operation.
15. Lift / Handle / Pull
Lifts, handles, or pulls are user-interface components that assist in operating the sash. Positioned on the bottom rail or stiles, they provide leverage and comfort during opening and closing.
Well-designed hardware reduces strain, improves accessibility, and contributes to the overall ergonomics of the window system.
16. Tilt Latch
Tilt latches allow sashes to pivot inward for cleaning or maintenance, commonly found in double-hung windows.
When released, they disengage the sash from the balance system while keeping it supported. Tilt latches improve safety and convenience without requiring exterior access to clean the glass.
Window Trim and Finishes
Trim covers gaps, enhances appearance, and protects vulnerable areas from weather damage.
17. Casing / Trim
Casing or trim surrounds the window frame where it meets the wall, covering gaps and providing a finished appearance.
Interior trim enhances aesthetics, while exterior trim protects the frame edges from moisture and air infiltration. Proper casing installation also contributes to insulation continuity and long-term durability.
18. Interior Stool
The interior stool is the horizontal ledge extending inward from the window sill. It provides a visual transition between the window and the interior wall and often serves as a small shelf.
Beyond aesthetics, the stool helps manage condensation and protects interior finishes near the window opening.
19. Apron
The apron is the decorative vertical panel installed beneath the interior stool. It conceals framing gaps and adds architectural detail to the window assembly.
While primarily aesthetic, the apron contributes to a polished interior finish and helps visually anchor the window within the surrounding wall space.
20. Drip Cap / Flashing
A drip cap or flashing is installed above the exterior head jamb to divert water away from the window. It prevents rain from seeping behind siding or trim, reducing the risk of rot and mold.
Proper flashing integration is essential for long-term moisture management and building envelope performance.
21. Brickmold
Brickmold is an exterior trim profile that frames the window and bridges the gap between the window frame and masonry or siding.
It provides a clean visual edge while protecting the perimeter from water intrusion. Brickmold is commonly used in traditional construction and replacement window installations.
Window Accessories
These optional components add decorative appeal, functionality, or specialized performance to the window system.
22. Grilles / Muntins
Grilles or muntins divide the glass area into smaller sections, either structurally or as simulated overlays. They enhance architectural style without necessarily affecting performance.
Modern grilles are often removable or placed between glass panes, allowing decorative flexibility while maintaining easy cleaning and insulation efficiency.
23. Mullion
A mullion is a vertical or horizontal structural element that joins multiple window units together. It transfers loads between adjacent windows and maintains alignment across the assembly.
Mullions enable larger window groupings while preserving structural integrity and consistent appearance across combined window openings.
24. Insect Screen
An insect screen is a removable mesh panel fitted into a window track or frame. It allows airflow while preventing insects and debris from entering the interior.
Screens are designed for easy removal, cleaning, and replacement, ensuring ventilation without compromising comfort or cleanliness.
25. Weep Hole
Weep holes are small openings located in the sill or frame that allow trapped water to drain to the exterior.
They are critical for moisture management, especially in sliding and fixed windows. Properly functioning weep holes reduce the risk of internal water damage and prolong the window’s lifespan.
26. Transom / Fanlight
A transom or fanlight is a fixed window positioned above a main window or door. It allows additional light into the space and often serves a decorative purpose.
While non-operable, transoms contribute to architectural character and can improve daylight distribution within interior spaces.
27. Spacer Bars
Spacer bars are structural components within insulated glass units that separate panes and maintain consistent spacing. They hold insulating gas in place and support the edge seal.
Modern warm-edge spacers reduce thermal bridging, improve energy efficiency, and help prevent condensation around the perimeter of the glass.
Maintenance Tips for Different Window Parts
Regular maintenance extends window life and performance. Simple cleaning and occasional lubrication prevent most problems. Catching minor issues early saves money on major repairs down the road.
- Clean weatherstripping with mild soap and water twice yearly, replacing any cracked or flattened sections immediately.
- Lubricate balance systems and crank operators annually with silicone spray to maintain smooth operation.
- Clear weep holes with a toothpick or small wire to prevent water backup and frame damage.
- Inspect IGU seals for condensation between panes, which indicates seal failure requiring glass replacement.
- Tighten loose hardware and adjust sash locks seasonally to maintain proper compression and energy efficiency.
To Conclude
Every window component plays a role in comfort, efficiency, and durability. From the sloped sill that sheds rain to the balance system that prevents slamming, these parts work as a team. Neglecting one affects the others.
Homeowners who understand their windows make smarter decisions. Replacing worn weatherstripping costs little but cuts energy bills noticeably. Spotting a failing IGU seal early prevents moisture damage to surrounding materials.
When repair or replacement time comes, knowing the vocabulary matters. Contractors respect informed clients. Supply stores can order the exact part needed. And DIY fixes become possible instead of intimidating.
Windows are just well-designed systems that anyone can learn to maintain and improve themselves.

